You won’t typically find a Hygon processor among the list of
best CPUs
For gaming or other uses, however, Hygon remains among China’s most significant fabless semiconductor firms. A hardware analyst notes this importance.
HXL
Recently unveiled an extensive plan outlining Hygon’s upcoming projects, which include a leading-edge 128-core, 512-thread processor.
The new server processor known as the C86-5G will come equipped with up to 128 cores along with simultaneous multithreading (SMT). The interesting part is that instead of following the usual two-way SMT (SMT2) found in most contemporary consumer and server processors, this chip uses a four-way SMT (SMT4) configuration. This allows for four threads per core, resulting in an impressive total of 128 cores and 512 threads.
Manufacturers have extensively employed different SMT configurations; Hygon isn’t presenting any groundbreaking ideas here. For example, Intel’s obsolete designs were based on similar approaches.
Xeon Phi
, particularly the
Knights Landing
Variant, featured an SMT4 design. Additionally, IBM’s Power8 processors support SMT4 functionalities and can go up to SMT8.
Hygon C86-5G Specifications
Unlike its predecessor, the C86-4G, which boasts half the number of cores and one-fourth the number of threads, the new C86-5G comes with double the cores and quadruple the threads. However, Hygon hasn’t revealed details about the exact microarchitecture used in this newer model; they have simply stated that it has undergone another upgrade. As such, the company asserts that the performance boost for instructions per cycle (IPC) from the C86-5G will be over 17% higher compared to its earlier version.
Hygon has made significant progress since its initial server processor, which was developed for the
Dhyana
The microarchitecture originates from AMD’s Zen IP. Nonetheless, it appears outdated now because according to Hygon’s product road map, after the C86-4G model, the firm switched to using a “newly developed proprietary architecture.” As such, the C86-5G is expected to feature an improved iteration of this undisclosed microarchitecture.
The C86-5G boasts a robust suite of features, featuring AVX-512 instructions along with support for 16-channel DDR5-5600, an upgrade from the previous model’s 12-channel DDR5-4800 setup found in the C86-4G. These enhancements enable the C86-5G to significantly enhance performance across various server and business tasks. Additionally, accommodating 16 memory channels means Hygon’s new platform could potentially manage vast amounts of data storage efficiently. Although the specific types of DIMMs supported were not disclosed by the manufacturer, as this is designed for servers, it likely supports RDIMMs among others. Even using standard DDR5 modules that max out at 64GB each, the C86-5G would be capable of utilizing up to 1TB of DDR5-5600 memory capacity.
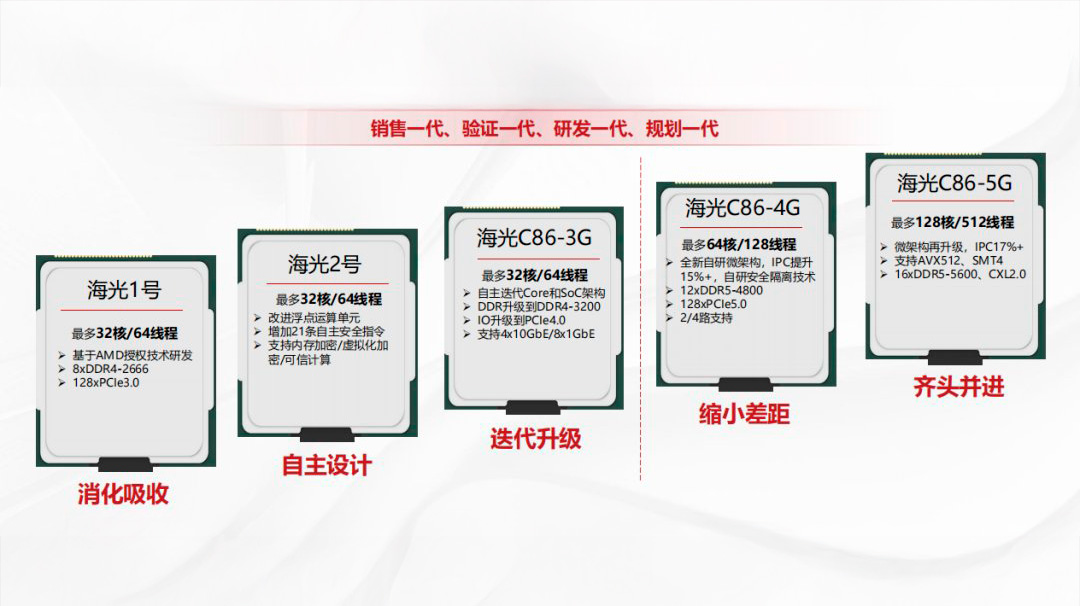
The earlier C86-4G model offers 128 PCIe 5.0 lanes for connectivity, matching the capacity of AMD’s fourth-generation
EPYC 7004
(codenamed Genoa) processors. While the exact count of PCIe 5.0 lanes available on the C86-5G remains undisclosed, Hygon has verified that this top-tier model will feature support for Compute Express Link 2.0 (CXL2.0), placing it in strong competition with the most recent offerings from AMD.
EPYC 9005
(codenamed Turin) and Intel’s
5th Gen Xeon
(codenamed Emerald Rapids) processors in terms of interconnect standards.
The
C86-4G
has presumably been available since last year, suggesting that Hygon probably began development on the C86-5G already. However, since the roadmap is quite ambitious and lacks specific dates, we cannot determine the current status of the C86-5G.
Before the
tariff conflict
with the U.S., China was already pursuing technological self-sufficiency. The tariffs merely accelerated the nation’s efforts to reach this goal, with companies like Hygon vital to the process. It’s unrealistic to believe Hygon can launch a chip that rivals AMD’s and Intel’s performance levels. Nonetheless, the C86-5G seems to compare well with competitors in terms of features, at least. Considering the current landscape, we expect to see C86-5G benchmarks soon.
Like this article? For more stories like this, follow us on MSN by clicking the +Follow button at the top of this page.